What Is On-Page SEO? A Guide to Optimizing for Search Engines
On-page SEO is the first step toward getting your website visible and ranking on search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo, etc.
It is the process of optimizing your website pages so that search engines can understand your content, allowing it to be easy and enjoyable to read for humans.
Think of on-page SEO as optimizing your website’s “engine” so that it can work better in search results.
SEO involves more than just inserting keywords or adding meta tags. Google has changed, and so have its algorithms. You now have to fit search intent, demonstrate expertise, and provide a great page experience to rank well.
How Search Engines Interpret Pages Today
Search engines are more intelligent than they have ever been. Gone are the days when Google ranked pages primarily based on keyword density.
Today, search engines use artificial intelligence and natural language processing to understand content quality, context, and intent.
-
Search Intent
There is always a reason someone searches. This could be to find new information, compare options, or they may be ready to purchase. Your content must fit that purpose.
For example, someone who searches “how to stop a dripping tap” is looking for a step-by-step guide, not a sales pitch for a plumber.
-
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
Google rewards content from trustworthy experts. Author bios, references to reliable sources, and evidence of experience all work to improve your page’s authority.
-
Page Experience Signals
These include the speed of your page, whether it is mobile-friendly, and how easily users can navigate your page without unwanted pop-ups. A positive page experience leads to higher user satisfaction and higher rankings.
Let us examine all of the key elements of on-page SEO and how each impacts your site’s visibility.
-
Keyword Research

Keyword research is the foundation of successful on-page SEO. It’s the process of figuring out what your audience is searching for and how they frame their search.
-
Short-tail and Long-tail Keywords
Short-tail keywords are general phrases like “SEO tips” or “digital marketing.” They tend to be highly searched for, but they also contain extremely high competition.
Long-tail keywords tend to be more specific, such as “best on-page SEO tips for beginners.” Long-tail keywords have fewer searches, which can often lead to more qualified traffic ready to engage or convert.
Keyword Types: Informational, Navigational, Commercial & Transactional
Knowing the intent behind the keywords will allow you to create the right kind of content.
1. Informational keywords: It is used when users seek knowledge.
- Example: “What is on-page SEO?”
- Ideal content: The informational keywords can be best used for blog posts, how-to guides, and FAQs.
2. Navigational keywords: These types of keywords are most effective when users search for a specific website or brand.
- Example: “Ahrefs blog” or “Moz keyword tool” or “Apple Store New York”
- Ideal content: The navigational keywords are most effective when you write an optimized homepage or about page.
3. Commercial keywords: These keywords are used by people comparing products or services.
- Example: “Best SEO tools 2025.”
- Ideal content: Commercial keywords prove effective for comparison posts, reviews, or listicles.
4. Transactional keywords: These keywords are used when someone is ready to make a purchase.
- Example: “Buy SEO software online.”
- Ideal content: Transactional keywords prove decisive when you include them in product pages, pricing pages, or landing pages.
Title Tags & Meta Descriptions

Image Source: searchenginejournal.com
The title tag presents users’ first impression of your page in the search results. Make it clear, descriptive, and include your primary keyword, preferably close to the beginning.
Example:
Title: “On-Page SEO Guide: Boost Rankings with Smart Optimization (2025)”
Meta descriptions aren’t direct ranking factors, but they can influence CTRs. They should give a summary of the page in about 150–160 characters, and naturally use your primary keyword phrase, while also creating curiosity or appeal for action.
Example:
“Find out how to get the most out of your site for search engines with established on-page SEO strategies from keywords to headings, UX to schema markup.”
Heading Tag Optimization (H1 to H6)
Headings organize your content and clarify its structure for humans and search engines.
- H1 – The main title of your page, typically your primary keyword used once.
- H2s & H3s – Subheadings that break the content down into readable sections.
- H4-H6 – Helpful for sub-points and lists in detail.
Don’t practice keyword stuffing. Focus on headings to improve the reading experience and to better guide the user through your content.
Content Quality & Depth
Even the best optimization cannot fix bad content. Quality, depth, and engagement will keep readers around and present authority to Google.
Here is what great SEO content is all about.
- It answers all user questions thoroughly.
- It is well-organized, contains small paragraphs, images, and/or bullet points.
- It uses plain language and includes relevant keywords as appropriate without overdoing it.
- It is original and trustworthy content, not just rewritten from someone else’s content.
When readers spend more time on your site page and engage with the content, Google takes this as an indication that your content is meeting their search needs.
Internal Linking
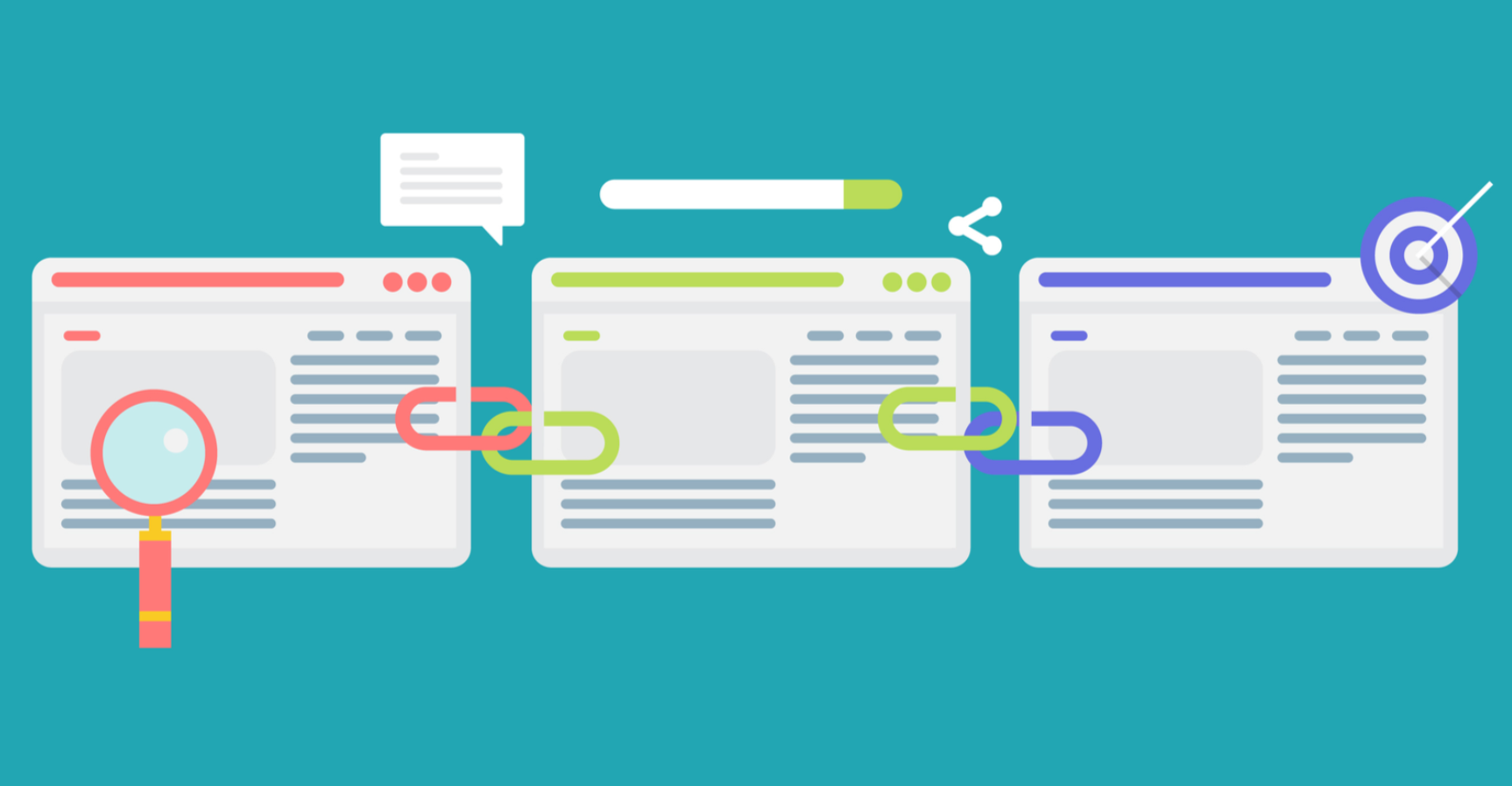

Image Source: searchenginejournal.com
Internal links are links between pages on your own site, and they help search engines crawl your site and pass ranking value (link equity) from one page to another.
As an example, suppose you have a blog post on “Keyword Research.” You could link that article to another article on “SEO Tools,” using descriptive anchor text that a user would understand. This helps build a web of context for Google, and encourages readers to follow links to learn more.
Suggestions for effective internal linking are: Utilize 3 to 5 internal links for every 1,000 words, Link to pages that are relevant and high-value, and Avoid generic or simple anchor text, such as “click here.”
Image Optimization
Images add life to your content, but can also slow down your site if not optimized. The key components of image SEO are file size, file name, title, and alt text.
URL Structure
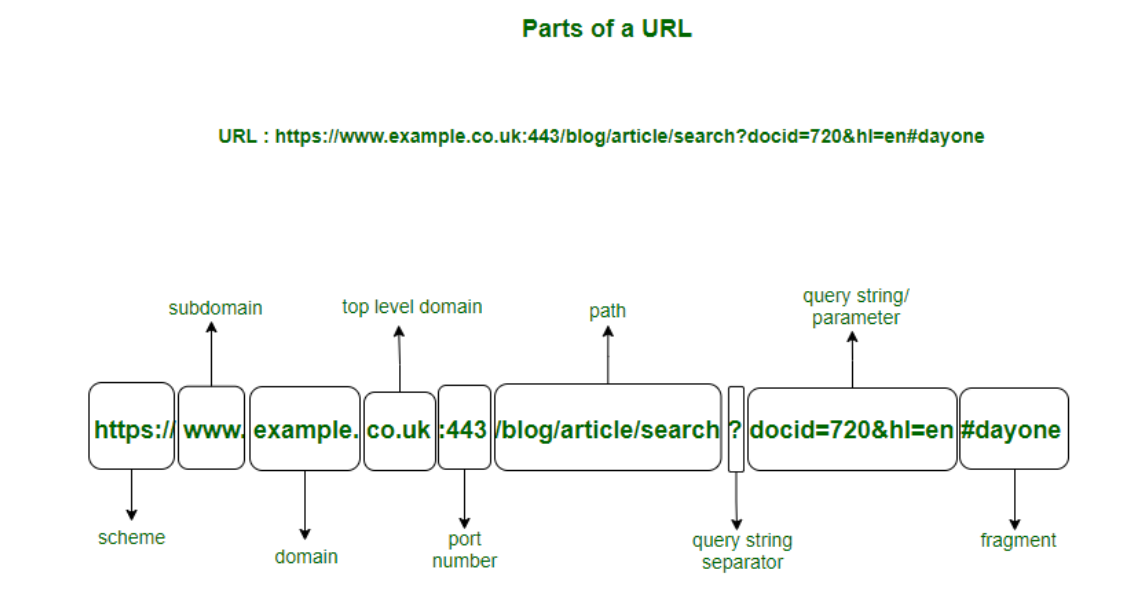
A clean and descriptive URL provides clarity to your users and search engines about the content of the page.
Best practices are to keep it short and easy to read, include your target keyword, use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_), and keep unnecessary parameters or symbols out of your URL.
Example:
www.yourwebsite.com/on-page-seo-guide instead of www.yourwebsite.com/page?id=12345.
Page Speed
Page speed is an important ranking factor. A slow site frustrates your visitors and generates higher bounce rates. Ways to increase page speed are as follows.
- Compress images and enable browser caching.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
- Reduce the number of JavaScript and CSS files.
- Choose a reliable and quick hosting service.
You can verify your site’s speeds using Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix and fix the suggested issues.
Mobile-Friendliness
With most users visiting your site on mobile devices, your site must be completely responsive. Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means it first looks at your mobile version to determine ranking.
You want to be sure your design adjusts to different screen sizes well, the text is easy to read, and the buttons are big enough to tap. A good mobile experience can significantly impact your engagement and ranking.
Wrapping It Up
On-page SEO is so much more than just adding keywords. It’s about providing a smooth experience for search engines and real humans alike. From your title tag to your internal links, every detail modifies how your page performs in the wild.
When you understand search intent and create valuable content, you meet user needs effectively. Ensuring your site is fast and mobile-friendly, as well as signal quality and relevance to Google.